User preferences in recommendation algorithms: the influence of user diversity, trust, and product category on privacy perceptions in recommender algorithms
Abstract
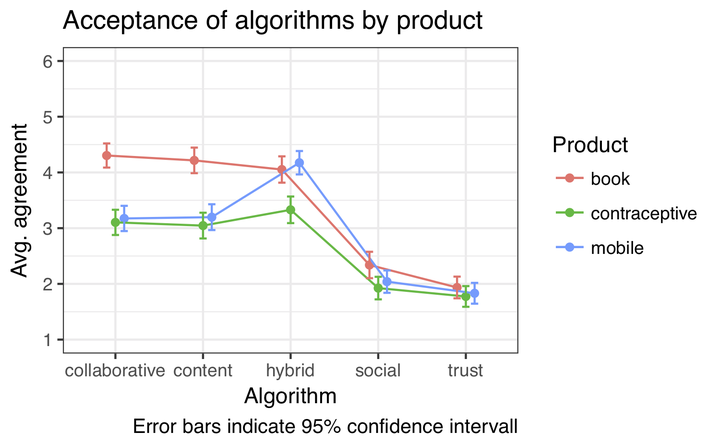
The use of recommendation systems is widespread in online com- merce. Depending on the algorithm that is used in the recommender system diferent types of data are recorded from user interactions. Typically, better recommendations are achieved when more detailed data about the user and product is available. However, users are often unaware of what data is stored and how it is used in recommendation. In a survey study with 197 participants we introduced diferent recommendation techniques (collaborative filtering, content-based recommendation, trust-based and social recommendation) to the users and asked participants to rate what type of algorithm should be used for what type of product category (books, mobile phones, contraceptives). We found diferent patterns of preferences for diferent product categories. The more sensitive the product the higher the preference for content-based iltering approaches that could work without storing personal data. Trust- based and social approaches utilizing data from social media were generally rejected.